
Logistics and Freight Outlook – May 2024
Sustainability in Transportation — An Enterprising Future
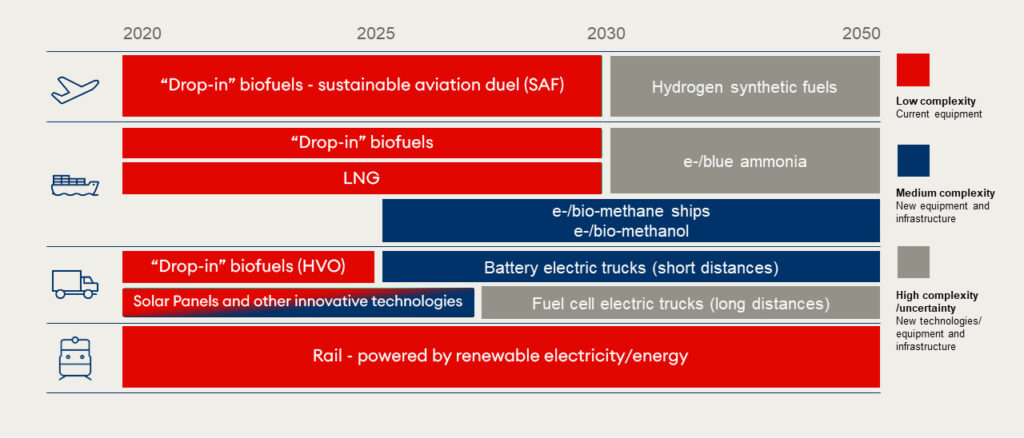
Overview of Challenges and Developments
There is an increasing necessity for sustainable freight transport options in supply chains, emphasizing that while automation boosts efficiency, the transition to clean technology presents its own set of challenges. Long-haul transportation, heavy trucking, and long-distance maritime and air transport still face significant hurdles despite advances in passenger electric vehicles.
Advances in Sustainable Fuels
There’s a significant push towards adopting cleaner technologies with investments in different pathways. The industry has introduced the first prototype fuel cell trucks and is utilizing low-carbon fuels such as second and third-generation biomass sources. However, scaling these technologies to make them cost-effective and widely available remains a challenge.
Path Toward Zero-Carbon Transportation
This section highlights the need for a mass balance approach to track and reduce carbon emissions effectively. It calls for a collaborative effort among businesses to innovate and create new models for zero-carbon transportation. Government intervention through regulatory measures and incentives is deemed essential to achieve these goals.
Insights into Ocean Freight – May 2024
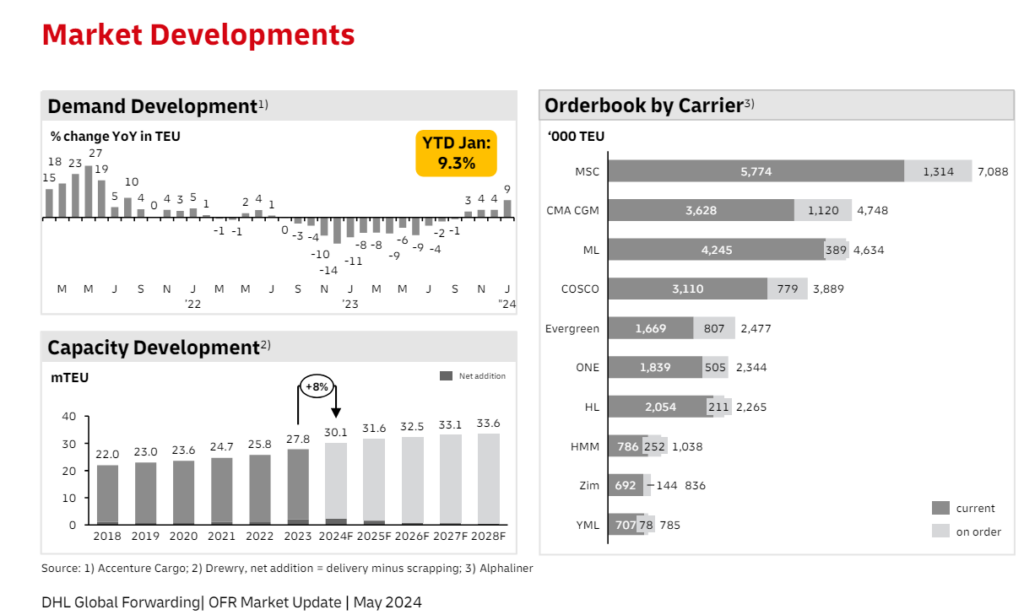
Key | |
++ | Strong Increase |
+ | Moderate Increase |
= | No Change |
– | Moderate Decline |
— | Strong Decline |
Outbound
Middle East – North America
High capacity meets rising demand for exports from the Middle East to North America.
Capacity — (+)
Rate — (+)
Middle East – Asia
The demand and capacity are balanced for this trade lane.
Capacity — (=)
Rate — (=)
Middle East – Europe
Extremely high capacity facilitates robust exports from the Middle East to Europe, with rising rates reflecting sustained demand.
Capacity — (++)
Rate — (+)
Middle East – Latin America
Export capacity is robust, matching a consistent increase in rates from the Middle East to Latin America.
Capacity — (+)
Rate — (+)
Inbound Updates
Asia – Middle East
The demand is greater than the capacity for this trade lane.
Capacity — (+)
Rate — (++)
North America – Middle East
Services like MECL and TP11 ensure reliability and efficiency in the India Sub-Continent/Middle East trade lane, despite dynamic market conditions.
Capacity — (=)
Rate — (=)
Latin America – Middle East
For Latin America trade lanes, capacity is decreasing due to operational challenges and port inefficiencies, while rates remain stable despite high demand.
Capacity — (-)
Rate — (=)
Europe – Middle East
The capacity is less than demand on this trade lane.
Capacity — (+)
Rate — (++)
Key Updates in Air Freight – May 2024
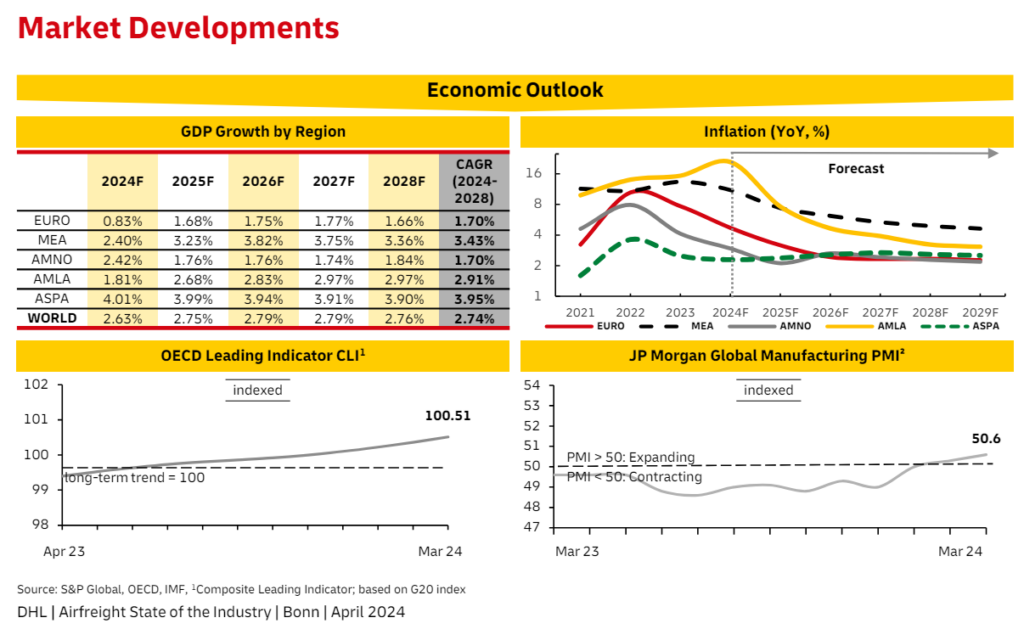
Demand: The demand for global air cargo expanded in April, which is now at +6% YoY in comparison to last year during the same time. The rise in e-commerce will increase the air cargo volume, which will mainly be led by the consumer and fashion sector. Furthermore, the Asia-Pacific routes rebounded, while the flows to Transatlantic declined.
Capacity: The air cargo capacity is at +10% YoY in comparison to April 2023. The growth in the capacity differs across the trade lanes due to influence of airspace closures, production shifts, and e-commerce expansion. Furthermore, amid the summer traffic season 2024, the Asia Pacific region is expected to increase the widebody belly capacity.
Rates: Due to the rise in global cargo demand and regional capacity challenges, the rate for airfreight continues to increase this month for some regions. The spot rates for Middle East and South Asia to Europe have increased quite a lot since April’23.
The Middle East and Air Carriers
The record rain in the UAE resulted in the temporary closure of DXB airport that caused +/-300 flights cancellations. The majority of the Dubai cargo backlog is now cleared after the capacity returns; however, delays can be expected. Moreover, the ongoing Red Sea conflicts have brought up tonnages by +153% compared to last year, amid the modal shift.
Asia
In Asia, the Red Sea challenges are boosting the sea-air conversion and capacity disruption. Specifically in India, the air cargo demand is rising due to the high demand for perishables, making shippers accept the costlier space. The surging e-commerce demand continues to affect AP routes to different regions, including Middle East, Europe, and United States.
Furthermore, Iran and Iraq conflict worsens the capacity issues, as the airlines have to reroute flights to avoid the impact. Lastly, the rates ex Asia have substantially increased and are expected to remain that way in May 2024.
America
There is a strong month-on-month increase in air volumes from BR, which could result in tight capacity to most of the destinations, including USA, EU, and AMLA. The USA-Latin America demand remains lower than the previous year’s level with adequate capacity. The US imports from India experience high demand, constrained capacity, and sharp rate increase.
In Latin America, the Mexican air imports of machinery parts and capital equipment are significantly increasing, indicating nearshoring.
Europe
As the key European markets continue to contract, the economic growth expectations in the Eurozone remain weak. The increase in the airfreight demand from UAE to Europe remains due to the Red Sea situation. Furthermore, there will be additional capacity outbound in Europe as a result of the 2024 summer schedule.
News Update on UAE Shipping – May 2024
CMA-CGM requests customers to accurately specify the Bill of Lading type at the time of Shipping Instruction submission to enhance service efficiency and avoid delays. Note that amendments post-vessel sailing will incur a fee. Read More
CMA CGM has announced new updates for Expiration of Port Congestion Surcharge (PCS) in Matadi, DRC. Learn More
ONE has recently announced a new advisory related to Demurrage and Detention Tariff update, which will be effective from 15th May 2024. Learn More
Global Factory Output – Overview
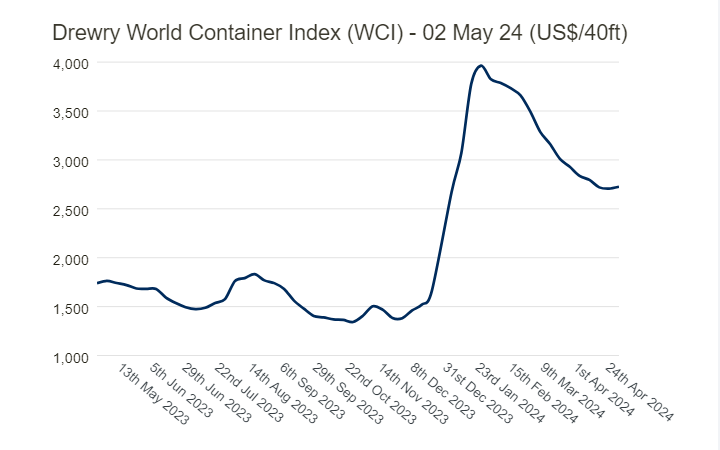
The value of the World Container Index increased by 1% at the beginning of May and has reached USD 2,725 per 40ft container.
United States of America (USA)
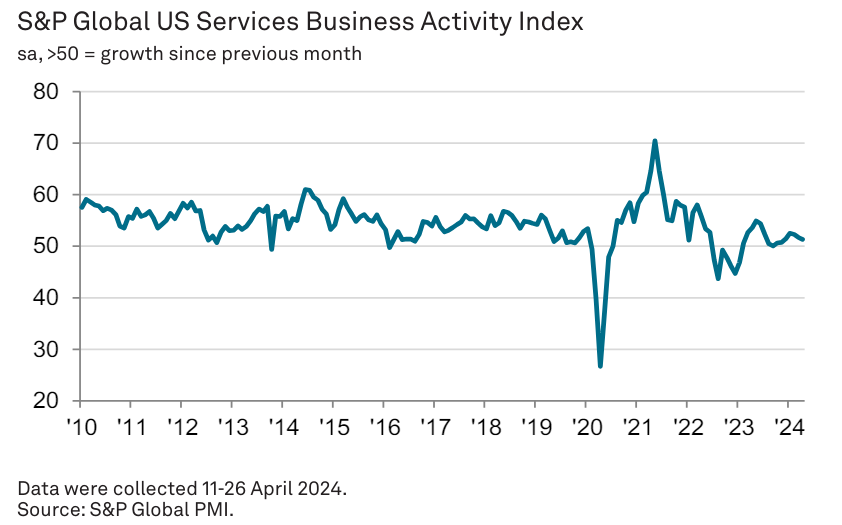
In April, the U.S. service sector growth slowed, leading to the weakest overall business activity of the year. This coincided with a slowdown in manufacturing output, with the GDP now projected to grow at a modest 1.5% rate in the second quarter. The decline in demand, the first in six months, reflects higher costs and expected sustained high interest rates, causing reduced business optimism and cautious staffing. However, inflation pressures eased as service prices rose at a slower rate due to increased competition and slower wage growth.
United Kingdom (UK)
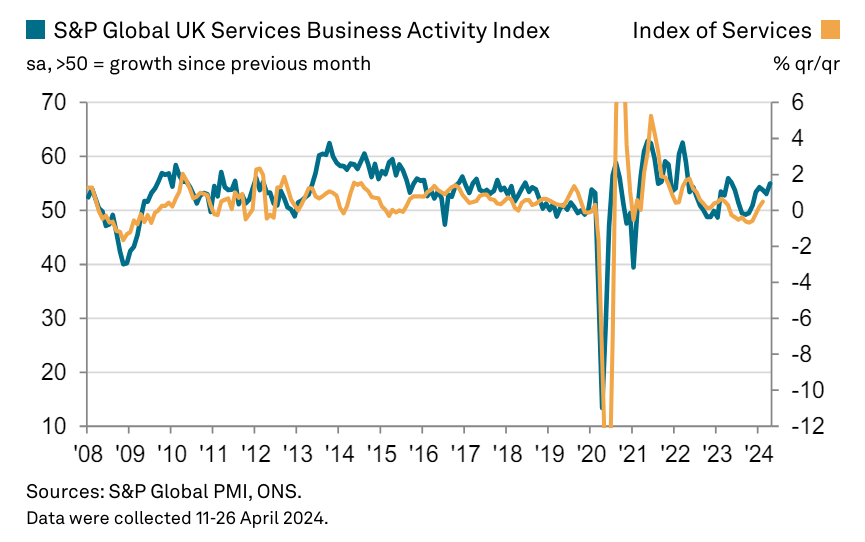
In April, the UK service sector recorded its most significant improvement since May 2023, driven by increased business and consumer spending. This activity suggests a quarterly economic growth rate of 0.4%, aiding recovery from last year’s recession. Despite optimism, high inflation led to cautious client spending, minimal job creation, and tight profit margins. Service price inflation hit a three-year low, even with rising business costs due to wage increases. Nonetheless, the sector remains optimistic about future growth, despite concerns about election uncertainty and unlikely interest rate cuts.
China
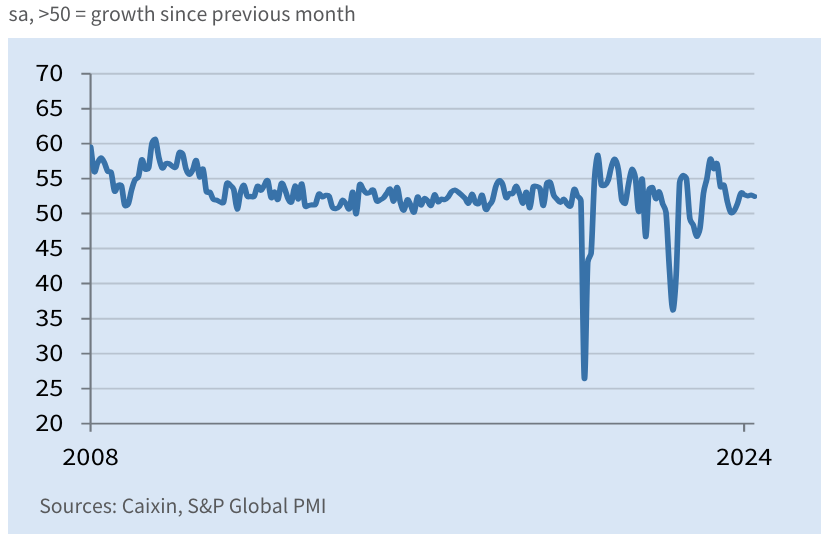
In April 2024, China’s service economy saw a moderate expansion, driven by the fastest growth in new business in nearly a year, improving overall activity and business confidence. Although employment continued to decline due to no capacity pressures, both input costs and output price inflation remained moderate. The Caixin China General Services Business Activity Index slightly decreased to 52.5 from 52.7 in March, marking 16 consecutive months of solid growth. Growth was supported by enhanced demand and expanded customer bases through business development efforts.
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
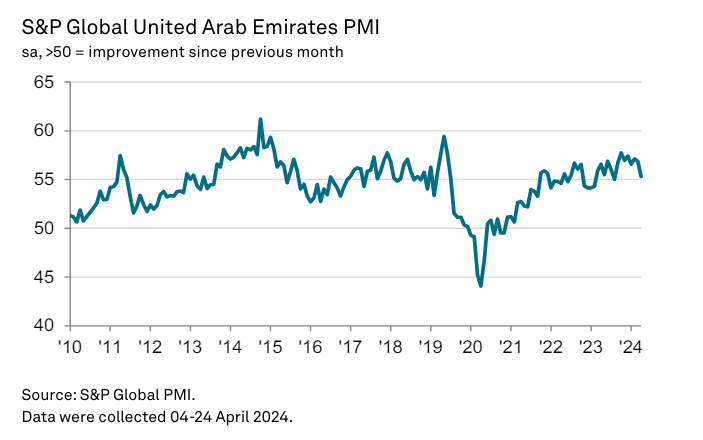
In April, the UAE’s non-oil private sector saw strong overall growth, though new business growth was sharply slowed by heavy rainfall and flooding, especially affecting Dubai. These weather disruptions led to increased backlogs and pressure on operating capacities. Despite this, non-energy businesses remained optimistic about their growth prospects, anticipating a quick recovery. Employment levels increased due to new projects and resilient demand, but price discounting continued to challenge operating margins, even as purchasing costs and salaries rose.
Related Articles
July 2025 Global Freight & Supply Chain
Middle East Ocean Freight and Port Operations Stable Operations with Ongoing Risk Monitoring Ocean f
Global Logistics and Shipping Update – June 2025
U.S. Revised Port Fee Regulations Impacting Chinese Maritime and Logistics Sectors The U.S. Trade Re
Global Logistics Market Update – May 2025
New Sulphur Emission Limits Enter into Effect in the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea officially






Post a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.