
The UAE and Saudi Arabia – Economic Powerhouses on the Rise

The bilateral trade relationship between the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia is characterized by a long history of economic cooperation and mutual investments. This trade partnership has yielded significant benefits for both countries, fostering economic growth, trade exchanges, and investment opportunities. In this overview, we delve into the trade history, current trade volumes, regulations, and key transportation routes between these two economic powerhouses. Furthermore, we explore the recent initiatives and advantages that make both the UAE and Saudi Arabia attractive destinations for investors.
Overview of Bilateral Trade between the UAE and Saudi Arabia
The trade relations between the two countries have been fruitful and have positive impact on several fields, including economic cooperation, joint investment, and trade exchange. Here’s a further breakdown of the trade between the two countries.
Trade History of the UAE and Saudi Arabia

The following is the data for the bilateral trade between the two countries:
United Arab Emirates – Saudi Arabia
The exports of United Arab Emirates to Saudi Arabia were recorded at USD 22.3 billion in 2021. The main exported products were Gold (USD 2.96 billion), Broadcasting Equipment (USD 1.57 billion), and Computers (USD 1.01 billion). In the span of 26 years, the exports of UAE to Saudi Arabia have increased at annual growth rate of 17.3%; i.e., USD 350 million in 1995 to USD 22.3 billion in 2021. Furthermore, Saudi Arabia was ranked as the third largest non-oil exporter of the UAE in the first six months of 2023.
Saudi Arabia – United Arab Emirates
In 2021, the total Saudi Arabia exports to the UAE were recorded at USD 14 billion. The main export products were Refined Petroleum (USD 4.61 billion), Ethylene Polymers (USD 893 million), and Special Purpose Ships (USD 783 million). In the last 26 years, the Saudi Arabia’s exports to the UAE have gone up at an annual rate of 12.4%, from USD 672 million in 1995 to USD 14 billion in 2021.
Current Trade Volume Between the two Countries

The trade volume between the two countries has reached AED 137.51 billion, increasing by 28% in 2022; in comparison to AED 107.41 billion in 2018. This has brought the total non-oil trade between the two countries to AED 586.75 billion over the last 5 years.
Based on the data provided by Ministry of Economy, in 2022, the trade between UAE and the Saudi Arbia included the imports of AED 34.31 billion; AED 36.01 billion in non-oil exports, and AED 67.18 billion in re-exports.
Trade Rules and Regulations
Rules & Regulations of Saudi Arabia
The importers of goods into Saudi Arabia must comply with the following regulations:
- The shipments must be accompanied by an original invoice, with quantity, quality, weight, and price details.
- Importers must get the import license from Saudi Arabian Ministry of Commerce and Investment before sending the shipment.
- A Certificate of Origin is mandatory, which must be endorsed by the relevant Chamber of Commerce.
- Certains products may be subject to restrictions that should be approved by the Ministry of Foreign Trade.
- The goods must also be accompanied by an import declaration, containing the details of importer, consignee, and the goods.
- The shipments should also contain an inspection certificate from a recognized laboratory.
- All the duties and taxes applicable on the goods must be paid off in advance.
- The importer should also submit the financial status and business operations related documents.
Rules & Regulations of The United Arab Emirates
Certain regulations are implemented for importation of different products. These regulations are important in order to maintain the quality, safety, and security of the shipments, country, and its citizens. Some of the rules and regulations in place are:
- Obtaining relevant license from the Ministry of Economy.
- Getting the import permits.
- Paying all the applicable duties and taxes before sending off the shipments.
- Ensuring that the shipment must fulfill the standards set by the Emirates Authority for Standardization and Metrology.
- Obtaining valid certificates of origin and invoices, along with correct marking and coding.
Top Export and Import of UAE and Saudi Arabia
Top Exports of Saudi Arabia
The top 5 exports of the Saudi Arabia are crude petroleum, refined petroleum, Ethylene Polymers, Propylene Polymers, and Acyclic Polymers. These products are usually being exported to China, India, Japan, South Korea, and United Arab Emirates.
Top Imports of Saudi Arabia
The most imported products for Saudi Arabia are Cars, Broadcasting Equipment, Refined Petroleum, Packaged Medicaments and Telephones. These are mostly imported from China, United Arab Emirates, United States, Germany, and India.
Banned Products in Saudi Arabia
There are a number of products that are banned into Saudi Arabia, including alcoholic beverages, pork and pork products, gambling items, narcotics, firearm and ammunition items, religious books or materials that are offensive to Islam, or any other items contrary to the regulations of Saudi Arabia.
Top Exports of the United Arab Emirates
Among the top exports of the UAE include crude petroleum, refined petroleum, gold, broadcasting equipment, and diamonds. Meanwhile, the leading exporters are India, Japan, China, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq.
Top Imports of the United Arab Emirates
The leading importer countries for the UAE are China, India, United States, Saudi Arabia, and Germany. Whereas the leading imported products are gold, broadcasting equipment, refined petroleum, diamonds, and cars.
Banned Products in the UAE
UAE has strict policy in place for the trading of banned products into the country. The list of such items includes illegal drugs, firearms, alcohol, and pork products. Furthermore, certain items such as food, drugs or cars require special permits.
Key Sea Ports
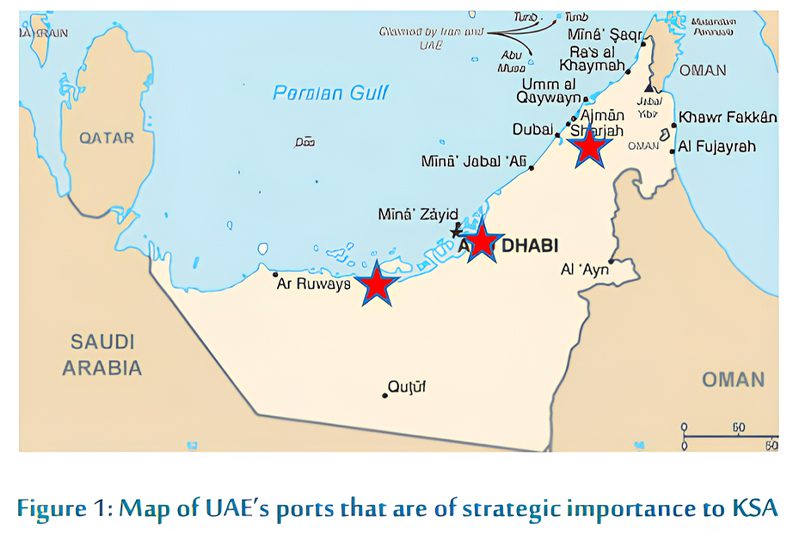
Sea Ports in the UAE
UAE has several seaports that are used for trading purposes, with Jebel Ali as the largest marine terminal in the Middle East. Below are further details of each port to identify their strategic importance for Saudi exports.
Port Name | Location | Cargo Handled |
Jebel Ali Port | Dubai | General Cargo |
Port Rashid | Dubai | General Cargo |
Khalifa Port | Abu Dhabi | General Cargo and Containers |
Port Zayed | Abu Dhabi | General and Bulk Cargo |
Port Khalid | Sharjah | General, Reefer, Dry, Liquid, and Bulk Cargoes |
Port of Hamriyah | Sharjah | General Cargo and Oil Tankers |
Port of Khor Fakkan | Sharjah | Containers |
Port of Fujairah | Fujairah | General Cargo, Bulk Cargo, Wet Bulk Cargo, and Container Handling |
Major Seaports in Saudi Arabia
Port Name | Location | Cargo Handled |
Jeddah Islamic Port | Jeddah | Livestock, Passenger Cargo, Bulk Grain, Containers, and General Cargo |
King Abdulaziz Port or Dammam Port | Dammam | Oil, General Cargo, Container, Bulk Grain, and Refrigerated Cargo |
King Fahad Industrial Port | Yanbu | Crude Oil, Refined Petroleum Products, Petrochemicals, Industrial Products, General Cargo, Containers, Ro-Ro-, and Bulk Cargo |
King Fahad Industrial Port | Al Jubail | Refined Petroleum, Chemical Fertilizer, Iron Ore Cargo, and Petroleum Gas |
Jubail Commercial Port | Al Jubail | General Cargo, Container, and Bulk Cargo |
Jazan Port | Jazan | Large Sized Cargoes, and Containers |
Ras al Mishab Port | Northeast Coast of Saudi Arabia | Container, Dry Bulk, and Break Bulk |
Ras Al Ghar Port | Northeast Coast of Saudi Arabia | Regional and Small Shipments |
Ras Tanura Port | Dammam | Mid-Size Cargo |
Dhuba Port | Northwest Area of Saudi Arabia | Passenger and Different Types of Cargo |
Major Airports in UAE and Saudi Arabia
Airports in Saudi Arabia
King Khalid International Airport – Riyadh (RUH)
The airport is located 35km north of Saudi Arabia’s capital city of Riyadh. There are 5 terminals in the airport, connected with each other through walkways. The Riyadh Airport has opened a Model Cargo Village in the support area of the airport that has the capacity of handling 600,000tpa of cargo.
King Abdul Aziz International Airport – Jeddah (JED)
King Abdul Aziz International Airport is the main gateway to Jeddah and just 65km to the west. The cargo center at the airport has a 75,000sqm cargo handling capacity that has a fully automated storage system, including 700 positions of Unit Load Devices (ULDs) and six Elevating Transfer Vehicles (ETVs).
King Fahd International Airport - Dammam (DMM)
The airport is located in Dammam, occupying a total area of 776km2. The cargo terminal of the airport is designed to handle 125,000t of cargo on a yearly basis. Another double-storey cargo building was opened in 2015 on an area of 39,500 m2, which can handle 94,000t of cargo every year.
Airports in the United Arab Emirates
Dubai International Airport (DXB)
The DXB is one of the biggest airports in the world that has the capacity of handling more than 3.3 million tonnes of cargo annually. The cargo terminal is known as a specialized center for flowers and plants as well as for handling advanced cargo.
Abu Dhabi International Airport (AUH)
The airport is known for handling large amounts of cargo, more than 13 million kg, weekly. The airport serves more than a hundred destinations across 56 countries.
Sharjah International Airport (SHJ)
The airport has 5 terminals dedicated to handling cargo. The terminals specialize in handling livestock and temperature-sensitive products along with general cargo.
Shipment Routes between UAE and Saudi Arabia
Major Transportation Routes from Saudi Arabia to the UAE – By Sea
Following are the main transportation sea routes from Saudi Arabia to the UAE
Route | Transit Time |
Jeddah Islamic Port to Jebel Ali | 5-6 Days |
Jeddah Islamic Port to Khor Fakkan | 4-6 Days |
Jeddah Islamic Port to Port Khalifa | 9-10 Days |
Jubail Port to Jebel Ali | 1-2 Days |
Jubail Port to Khor Fakkan | 3-4 Days |
King Abdul Aziz Port to Jebel Ali | 1-2 Days |
King Abdul Aziz Port to Khor Fakkan | 3-4 Days |
King Abdul Aziz Port to Port Khalifa | 23-44 Days |
King Abdullah City Port to Jebel Ali | 7-8 Days |
King Abdullah City Port to Khor Fakkan | 6-7 Days |
Land Ports Between the UAE and Saudi Arabia
The bilateral trade between the Arab countries, including UAE and Saudi Arabia is usually carried out by road. Therefore, the land ports have a key role in the advancement of trade relations between the Arab countries. In case of Saudi Arabia and the UAE, there is only one crossing border, which is Al Ghuwaifat (UAE) and Batha (Saudi Arabia). The General Administration of Customs in Abu Dhabi acts as an overseeing authority in the UAE; whereas, in Saudi Arabia, the same role is played by the Saudi Customs.
Major Transportation Routes from Saudi Arabia to the UAE – By Air
Following are some of the major transportation routes by air that are used to transfer goods from the UAE to Saudi Arabia:
Origin | Destination | Transit Time |
Dubai International Airport (DXB) | Riyadh Airport (RUH) | 1-2 Days |
Dubai International Airport (DXB) | Jeddah Airport (JED) | 1-3 Days |
Dubai International Airport (DXB) | Dammam Airport (DMM) | 1-2 Days |
Abu Dhabi International Airport (AUH) | Riyadh Airport (RUH) | 1-2 Days |
Abu Dhabi International Airport (AUH) | Jeddah Airport (JED) | 1-2 Days |
Abu Dhabi International Airport (AUH) | Dammam Airport (DMM) | 1-3 Days |
Sharjah International Airport (SHJ) | Riyadh Airport (RUH) | 1-4 Days |
Sharjah International Airport (SHJ) | Jeddah Airport (JED) | 1-2 Days |
Import Documents Required to Enter into UAE
For the products like Building Materials, Chemicals and Polymers, Food Products, Packages, Consumer Durables, Heavy Machinery and Electronics, Precious Metals & Jewelry, Pharmaceuticals, and Textiles, you’ll need the following documents:
- Certificate of Origin – procured from the relevant authorities.
- Commercial Invoice – procured from the exporter.
- Packing List – procured from the exporter.
- Ocean Bill of Lading/ Truck Waybill – procured from the transport company.
- Delivery Order – procured from the transport company.
- Trade License – procured from the relevant authorities.
- Statistical Statement – procured from the relevant authorities.
Additional Documents
Products | Import Permit | Halal Slaughtering Certificate | Phytosanitary/Health Certificate | Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product |
Building Materials | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Chemicals and Polymers | ✔
| ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Food Products | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ |
Packages | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Consumer Durables | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Heavy Machinery and Electronics | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Precious Metals & Jewelry | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Pharmaceuticals | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔ |
Textiles | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Government Agencies in the UAE for Trade
The following are the government agencies that play significant role in the trade from and to the UAE.
Federal Customs Authority
This government entity is responsible for developing and implementing the customs procedure at a national level, along with regulating the customs process in the UAE.
Abu Dhabi Chamber of Commerce
They are responsible for developing the commercial trade activities in the emirate of Abu Dhabi.
Abu Dhabi General Administration of Customs
As the name suggests, this entity is responsible for administrating the customs procedure.
Department of Economic Development – Abu Dhabi
This entity is responsible for proposing economic and commercial policies to facilitate trade activities.
Abu Dhabi Ports Company
They are responsible for developing the port facilities to improve the trade conditions.
Dubai Customs
The Dubai Customs authority is responsible for administrating the customs procedure in Dubai.
Department of Economic Development – Dubai
This government entity is responsible for preparing and implementing the economic plans.
Dubai Chamber
This government entity is responsible for issuing trade documents, like Commercial Documents or Certificate of Origin.
Dubai Trade
Dubai Trade is responsible for making interregional and international trade easier and smoother.
Sharjah Chamber of Commerce and Industry
This entity is responsible for issuing trade documents, such as commercial documents, or other required certificates, etc.
Department of Seaports and Customs
They are responsible for controlling and managing the movement of goods and provide the relevant port facilities.
Sharjah Customs
This custom authority supervises and controls the movement of goods, entering or exiting Sharjah.
Economic Development Department – Sharjah
They develop and implement the relevant economic plans required to improve the trade conditions in Sharjah.
Government Agencies in Saudi Arabia for Trade
Following government agencies play a vital role in the trade from and to the Saudi Arabia.
General Authority for Foreign Trade
This agency is responsible for boosting international commercial and investment activities in Saudi Arabia.
Ministry of Investment
The ministry oversees the foreign investment in the country along with issuing licenses to the foreign investors.
Saudi Export Development Authority
This is an organ of the Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources that is responsible for developing country’s export industry in the non-oil sector.
Capital Markets Authority
This government financial regulatory authority is responsible for capital markets in the country.
Saudi Authority for Intellectual Property
This official government body is responsible for protecting and supporting the intellectual property in Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Ports Authority
The purpose of this government agency is to bring together the operations of multiple ports of the country to one office.
Ministry of Commerce and Investment
The agency’s responsibilities include developing and implementing the policies and mechanisms that govern the commerce and investment sector.
Why Invest in Saudi Arabia?
As the economy of Saudi Arabia continuous to stabilize, significant opportunities are available for the investors. In the following section, we will explore some of the advantages and possibilities of investing in Saudi Arabia:
Strategic Location
Saudi Arabia has strategic location since it acts like a major gateway to the Middle East, Africa, and Asia that have some of the fastest growing markets in the world. Furthermore, the country has well-established transport, telecommunications, and logistics infrastructure. This makes it easy for the investors to access these regions.
Diverse Initiatives

The Kingdom’s government has started an initiative known as Vision 2030 that will reduce the country’s dependency on oil and gas revenues. This plan will give boost to the new sectors, such as health, tourism, technology, and entertainment.
Big Consumer Market
Saudi Arabia has a young and growing population that has a rising disposable income. Saudi Arabia has large reserves of oil that has helped boosting the economic growth and consumer spending. Furthermore, the retail sector has significantly grown over the last decade, including the e-commerce sector.
Business- Friendly Environment
Saudi Arabia has taken several initiatives and introduced reforms that has improved the investment environment significantly. The government of the country has eased the restrictions on foreign ownership, simplifying the licensing process and creating incentives for foreign investors. Based on the data released by the World Bank in 2020, Saudi Arabia jumped 30 places in the ranking of ease of doing business, showing significant progress over the years.
Recent Initiatives
Revolutionizing Investment Equality
In January 2022, the Ministry of Investment introduced a groundbreaking investment framework designed to level the playing field for both local and foreign investors. The primary objective is to invigorate investment across diverse economic sectors by fostering an appealing and equitable environment, safeguarding investors’ rights, and bolstering their confidence. This transformative approach entails key measures such as non-discrimination, granting investors the freedom to manage their projects, streamlining administrative procedures, and facilitating fund transfers. Moreover, the system ensures the protection of intellectual property, commercial information, and personal data, all while upholding principles of fairness and transparency.
Pioneering National Investment Strategy
In alignment with its Vision 2030, the Kingdom embarked on the implementation of the National Investment Strategy unveiled in October 2021. This strategy serves as the guiding framework for advancing the nation’s investment landscape, aiming to amplify the Kingdom’s standing on the global investment stage. Key objectives include diversifying the national economy, fostering knowledge and expertise localization, and nurturing investments in burgeoning sectors. This multifaceted plan revolves around three core goals: enhancing the private sector’s influence on the balance of payments, bolstering the growth of strategic industries, and elevating the investment ecosystem. It harmonizes both new and existing initiatives, such as the Shareek Program and the Regional Headquarters Attraction Program, to create premium investment prospects, optimize their utilization, and elevate the Kingdom’s competitive position on regional and global fronts.
Modernizing Data Protection and Business Services

Saudi Arabia has taken significant steps towards digitization and transparency. In March 2022, the nation introduced the pioneering Data Protection Regulation, marking a pivotal stride in fortifying the legislative framework essential for supporting the burgeoning digital economy. Simultaneously, the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority revealed the “Fatoorah” e-invoicing platform, a pivotal element in the comprehensive digital transformation strategy aimed at streamlining business services. A resolute anti-commercial concealment campaign was also launched to enhance the business environment’s appeal to foreign investors and ensure corporate compliance and transparency.
Global Supply Chain Resilience Initiative
The Kingdom’s Global Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (GSCRI) is a visionary endeavor designed to lure investors to Saudi Arabia. It revolves around the identification of investment opportunities, the establishment of special economic zones, and the attraction of international corporations. This strategic initiative prioritizes sustainability, climate change responsiveness, the enablement of future industries, global supply diversification, and the advancement of cutting-edge sectors. With a substantial stimulus budget of $2.7 billion, the GSCRI aspires to entice $10.7 billion in industrial and service investments within a two-year span. It leverages the Kingdom’s inherent competitive advantages to empower investors in realizing their investment ambitions and attaining success.
MIZA Service Initiative
As part of the National Investment Strategy, the Kingdom rolled out the MIZA initiative, offering a comprehensive suite of financial, tax advisory, and business services to support investors in exploring opportunities within the Saudi market. This initiative extends its support to local and international investors, guiding budding entrepreneurs, providing logistics assistance, and facilitating companies interested in establishing regional headquarters within the Kingdom.
Why Invest in the UAE?
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has emerged as an increasingly appealing investment destination, offering abundant opportunities across a multitude of sectors. This summary provides a concise insight into the compelling motives for considering investments in the UAE, drawing insights from various sources.
Strategic Location
Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, the UAE serves as a global business hub. It functions as a gateway to over 2 billion consumers, thus facilitating international trade and investment on a grand scale.
Economic Diversification
The UAE has proactively diversified its economy beyond its historical reliance on oil. It has shifted its focus towards robust sectors such as tourism, technology, and renewable energy. This diversification has significantly reduced the nation’s dependence on oil revenues, contributing to enhanced economic stability.
Business-Friendly Environment
The UAE prides itself on its pro-business environment, marked by minimal bureaucracy, favorable tax policies, and a range of incentives for foreign investors. Free zones offer the attractive prospect of 100% foreign ownership, simplifying the process of setting up businesses.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
The UAE boasts world-class infrastructure, encompassing state-of-the-art airports, ports, and road networks, which substantially support the seamless functioning of businesses. The nation’s connectivity is a vital asset, ensuring efficient global trade.
Political Stability and Security
The UAE has gained acclaim for its enduring political stability and unwavering commitment to safety. These factors render it an ideal location for long-term investments, inspiring confidence among investors.
Expo 2020 and Vision 2030

Dubai’s hosting of Expo 2020 has created a platform for showcasing innovation, culture, and numerous investment opportunities. This event has drawn businesses and investors from around the world, fostering collaboration and growth. Furthermore, Abu Dhabi’s Vision 2030 is a forward-looking initiative that centers on economic diversification, sustainable development, and innovation, presenting substantial investment prospects in various sectors.
Tech and Innovation Hub Enhancing Quality of Life
The UAE offers a superlative quality of life for both residents and expatriates, with exceptional healthcare, educational, and leisure facilities that attract a skilled workforce and talented individuals. The nation’s investment in becoming a regional tech and innovation hub, featuring initiatives like Dubai Internet City and Area 2071, is fostering innovation-driven growth and adding to the appeal of the UAE as an investment destination.
Conclusion
The trade ties between the UAE and Saudi Arabia continue to strengthen, underpinned by mutual economic interests and ongoing cooperation. The trade volumes have surged, reflecting the resilience and dynamism of these economies. Moreover, both countries have taken significant steps to streamline trade regulations and enhance the business environment, making it easier for investors and entrepreneurs to participate in this thriving partnership.
The strategic locations, diversification efforts, burgeoning consumer markets, and business-friendly environments in both the UAE and Saudi Arabia offer compelling reasons for investors to consider these nations for their ventures. Recent initiatives, such as Saudi Arabia’s groundbreaking investment equality framework and the UAE’s Expo 2020 and Vision 2030, further underline the commitment of these nations to economic progress and innovation. With their well-established infrastructure and connectivity, political stability, and focus on technology and innovation, the UAE and Saudi Arabia stand as attractive destinations for investors seeking growth and opportunities in the Middle East and beyond.
Related Articles
Exploring the Booming UAE-Indonesia Economic Relations
The economic relations between the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Indonesia have been flourishing in
Comprehensive Guide on USA-UAE Economic Relationship
Introduction The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been a central player in the realm of international
The UAE and Saudi Arabia – Economic Powerhouses on the Rise
The bilateral trade relationship between the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia is characte






Post a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.