
Dedicated Dangerous Goods Facility in Dubai
Dangerous goods (DG) are hazardous or prohibited items with flammable, non-flammable, poisonous, or radioactive properties. However, improper handling during storage and distribution can cause health and safety risks to people, animals, and the environment.
For this reason, there are storage areas designed especially for these goods. A dangerous goods facility ensures the appropriate warehousing of substances labeled as explosive, toxic, or flammable and items like aerosols, perfumes, and lithium batteries.
Regulatory authorities like the Dubai Municipality (DM), Dubai Health Authority, and the DCD enforce regulations to guide the storage of these peculiar goods. Surely, DG warehouses are crucial in UAE logistics so, this comprehensive guide discusses these specialized facilities in detail.
Key Features and Functions of Dedicated Dangerous Goods Facilities
Facility Design and Layout
The facility design and layout of a dangerous goods warehouse indicates the various measures taken toward handling and storage of hazardous materials. Before obtaining a DM Warehouse Approval, a facility must meet specific requirements as follows:
- The site location is for industrial work.
- The building layout should provide adequate natural ventilation and lighting.
- Canteens, changing rooms, and restroom for warehouse employees.
- Sufficient perimeter fencing and vehicle parking space.
- EHS standard smoke detectors in all partitioned areas within the facility.
Complying with ISO45001 and ISO14001 codes ensure the establishment of efficient working environments. Also, sprinklers/foam systems, extinguishers, and spill containment kits guarantee rapid response for onsite emergencies.
Segregation and Containment
Segregation and containment are warehousing practices that ensure safety in a dangerous goods facility.
Hazardous materials occupy different zones/compartments across any area. dedicated storage warehousing This separation keeps potentially reactive substances apart, for instance, segregating acids from bases.
Containment measures deal with risks from accidental spills or leaks within the premises. Spill/drip trays and leak-proof containers keep the environment clean. Also, standard Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) reduces the risks of personal injury.
Safety Equipment and Infrastructure
The following are various safety features that protect warehouse staff and prevent accidents:
- Ventilation – Manages interior air quality within the warehouse by removing dispersed fumes or vapors from toxic gases or liquids.
- Fire Suppression Systems – Detect and reduce damage from hazards. Examples are Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus (VESDA), sprinklers, and foam systems.
- Personal Protective Equipment – Includes specialized clothing and accessories worn by warehouse personnel to prevent burns from fires or inhaling toxic gases. These include safety goggles, boots, full-on HAZMAT suits, and gloves.
Hazardous Materials Handling Procedures
Key considerations when handling hazardous materials in a dedicated facility include:
- Proper building layout to store materials in separate zones depending on compatibility.
- Efficient stacking and traffic flow systems to reduce collisions of containers.
- Enforcing PPE for personnel responsible for unloading, moving, or stacking dangerous goods.
- Appropriate waste management and disposal according to regulatory codes.
- Dedicated emergency stations to provide shelter during shutdown or evacuation procedures and provide emergency first aid services.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Dangerous Goods Handling
Dubai's Regulatory Authorities
The Dubai Civil Defense (DCD) enforces regulations for storing, handling, and transporting dangerous goods within the Emirate. The Hazardous Substances Control Department conducts inspections, issues permit, and offers the necessary guidelines.
Also, the UAE’s Securities Industry Regulatory Authority (SIRA) can ban or restrict certain hazardous materials and enforce import/export compliance.
The Dubai Municipality and the Dubai Health Authority (DHA) also uphold city-wide measures regarding hazardous items to safeguard human and environmental health.
Licensing and Permitting Requirements
For operating a dedicated dangerous goods facility in Dubai, the appropriate licensing and permit requirements include
- Warehouse Approval from the Dubai Municipality for compliance with building regulations and design guidelines.
- Environmental and Health Safety Department (EHS) license for operating a warehousing facility.
- Approval from the Dubai Police to move explosives, military equipment, and weapons within Dubai.
- Prior approval from the Ministry of Health (MoH) before importing and storing controlled chemicals.
Others are Good Warehousing Practices (GWP) and Ports, Customs, and Free Zone Corporation (PCFC) requirements for DG storage and distribution.
Documentation and Reporting
Up-to-date Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and copies of all relevant permits and licenses are vital for moving dangerous goods within Dubai. These should also include transport clearances from the applicable authority (DCAA, Dubai Customs, among others).
When spills or leaks occur, notifying the DCD Operations Center or Emergency Services allows for prompt investigation and implementation of corrective measures.
Storage and Handling Practices for Dangerous Goods
Classification and Segregation of Dangerous Goods
Dangerous goods fall into various groups, which are:
- Explosives such as ammunition dynamite and fireworks
- Flammable, non-flammable, or toxic gases, like propane and CO2
- Liquids like ethanol and diesel fuel that are flammable
- Flammable solids and materials that combust spontaneously or release explosive gases when in contact with water e.g matches, potassium
- Oxidizing substances
- Toxic and infectious substances, including pesticides
- Radioactive materials and medical equipment
- Chemically reactive or corrosive substances, like caustic soda and hydrochloric acid
- Miscellaneous dangerous goods e.g., lithium batteries, magnetized materials, and asbestos.
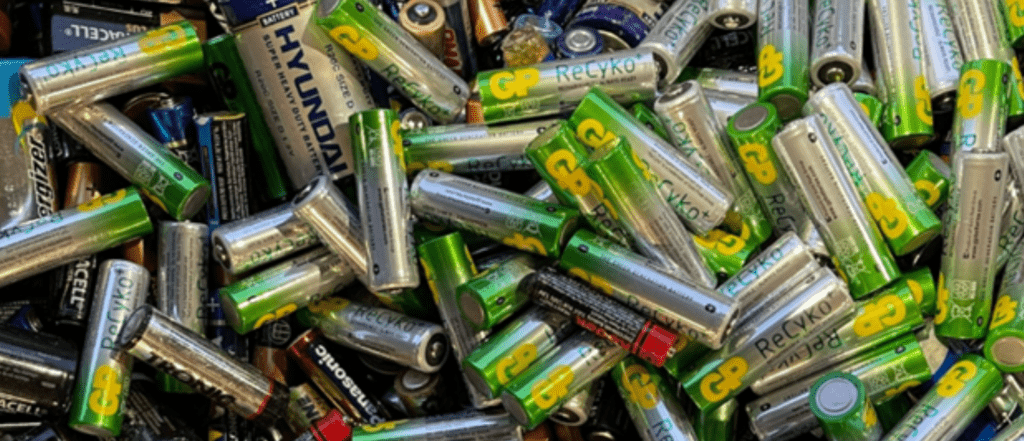

It’s critical to separate potentially reactive or incompatible substances e.g., oxidizing substances and flammable liquids/gases.
Storage Conditions and Temperature Control
Storage conditions will vary depending on the particular substance. Some helpful guidelines are:
- Storing flammable liquids and solids away from heat or open flame, sparks, and other sources of moisture.
- Segregating oxidizing substances from flammable/combustible substances and other reactive materials.
- Using acid-resistant containers for corrosive substances.
- Implementing material-specific temperature control to prevent very high or low temperatures.
- Following the manufacturer and regulatory guidelines for handling any hazardous materials.
Emergency Response and Incident Management
Accidents are sometimes inevitable when dealing with dangerous items.
Still, emergency response plans and incident management protocols in warehouses comprise the following; hazard assessment, external emergency contacts, cleanup, alarm and detection systems, training and education of warehouse personnel, and incident reporting procedures.
These elements address the particular safety needs of each facility. So, proper implementation reduces the day-to-day risks associated with hazardous materials storage.
Training and Certifications for Personnel
Training Requirements for Personnel
By law, all warehouse employees must undergo appropriate training before partaking in storing, handling and distributing dangerous goods. Essential requirements of this education process are:
- Identifying the various classes of harmful goods, and the associated risks.
- Proper packaging, marking, and labeling of warehouse items.
- Storage, stacking, and segregation procedures.
- Wearing PPE within the facility premises.
- Understanding the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS).
- Reporting incidents and dealing with emergencies
Dangerous Goods Regulation (DGR) courses ensure that working professionals understand the risks associated with DG storage and distribution.
Ongoing Training and Skill Development Ongoing or regular refresher training is crucial for warehouse staff to stay up-to-date on evolving safety regulations, DG storage standards, and entirely new substances. Mock drills can help build emergency preparedness against future incidents.
Additionally, some employees may need function-specific training. Together with basic awareness programs, this training helps to inculcate skills necessary to maintain a DG warehouse.
Benefits and Considerations of Dedicated Dangerous Goods Facilities
Enhanced Safety and Compliance
Dedicated dangerous goods facilities in meeting safety standards and comply with regulations in the following ways:
- Hazard-resistant building design and construction.
- Well-trained and competent staff for identifying, unloading, shelving, and transporting hazardous materials.
- Use of specialized safety equipment and infrastructure e.g., personal protective equipment, first aid kits, fire extinguishers, spill containment measures, and adequate ventilation
- Well-labeled and segregated storage zones for holding varying classes of goods.
Risk Mitigation and Liability Management
To reduce the risks and potential liability associated with chemical storage, operations in a typical DG warehouse incorporate the below strategies:
- Recognizing the impact of chemical properties and storage conditions on the possibility of fire hazards.
- Reviewing operational standards to reduce fines or penalties due to non-compliance.
- Obtaining special insurance coverage (product, pollution, or general liability insurance) against financial losses due to hazard-related incidents or damage.
- Planning emergency procedures when necessary, e.g., evacuation or shutdown
Continuous reevaluation is necessary to account for newly introduced materials or evolving restrictions (or other rules) affecting hazardous substances.
Streamlined Operations and Efficiency
Besides complying with industry regulations and guaranteeing worker safety, dedicated DG facilities encourage efficient warehouse operation through these features:
- Well-organized shelves and aisles to facilitate easy storage and retrieval of goods.
- Segregation of hazardous materials by class and compatibility to rapidly track similar cargo and perform safety inspections.
- Integration of automated warehousing systems and RFID technology helps to count stock in real-time and simplify order fulfillment procedures.
How Al Sharqi Can Help
Hazardous materials logistics in Dubai is impossible without a dedicated dangerous goods facility.
But for your import/export business, you don’t need to worry about building your warehouse. Outsourcing to a 3PL, like Al Sharqi, helps companies be flexible in their storage and distribution procedures.
At Al Sharqi, our strategic facility locations ensure secure storage at reduced costs. Contact us today to access top-quality warehousing solutions for Dubai and the rest of the UAE.
Conclusion
Dedicated warehouses are crucial in storing and distributing dangerous goods. Factors like unique building design, safety features, and hazard suppression systems contribute to enhancing the safety of workers and the surroundings.
Additionally, compliance with state-wide regulations creates an efficient working environment, with proper measures to handle accidents and dispose of wastes.
Ultimately, the safety of human lives and properties is the priority. So, businesses dealing with dangerous goods should utilize standard DG warehouses that keep Dubai safe for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
A dedicated dangerous goods facility is a storage area specifically equipped and reserved to hold all categories of harmful cargo. These cargoes include explosive and poisonous substances, aerosols, perfumes, and products containing lithium batteries.
Dedicated facilities for storing dangerous goods should have fire-resistant construction, hazard detection and suppression devices, emergency stations, adequate ventilation, and appropriate waste disposal systems.
The building construction must contain fire-resistant materials, warehouse personnel should use appropriate PPE when handling goods, and receive relevant training to tackle potential hazards. Also, the disposal of hazardous waste must follow DCD regulations.
Operating a DG storage facility requires warehouse approval from the Dubai Municipality, EHS and PCFC permits, and approval from the Ministry of Health. Distribution within Dubai may require further clearance from the Dubai Police or the UAE’s Securities Industry Regulatory Authority.
Our customer service team is happy to assist you with planing your next booking.

Related Articles
What Products Require Climate Control Storage in Dubai?
As temperatures soar in the Gulf region, reliable and efficient storage solutions is now a priority.
Short-term Vs Long-term Storage in Dubai
Short-term storage involves safekeeping inventory for a limited time, it can usually be for days to
Healthcare Storage Solutions – What Do They Have To Offer
The health industry needs efficient storage as they work with sensitive medical inventories. As a re






Post a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.